Types of Heart Attacks: STEMI and NSTEMI
What is a Heart Attack?
Heart attacks, medically termed myocardial infarctions (MIs), are among the most urgent medical emergencies worldwide. With the American Heart Association reporting a heart attack every 40 seconds in the United States, awareness and understanding are key.
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked or significantly reduced, often due to a blood clot in the coronary artery. This event can lead to serious, sometimes fatal, damage to the heart muscle.
Heart attacks are alarmingly common, with approximately 805,000 new cases and 200,000 recurrent attacks annually in the U.S. alone. Recognizing their signs and understanding treatment options is vital for survival and recovery.
Types of Heart Attacks: STEMI and NSTEMI
Heart attacks can manifest in two primary forms: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI).
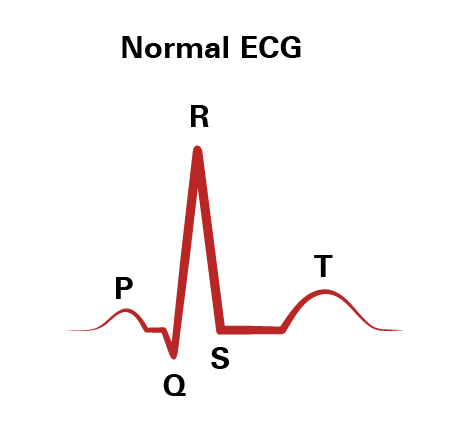
- P Wave: Electrical activity of the atria (upper chambers of the heart) as they contract
- QRS Complex: Electrical activity of the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart) as they contract
- T Wave: Re-polarization or recovery of the ventricles
STEMI: A Severe Heart Attack
STEMI, or ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, is a severe form of heart attack. It occurs when there's a complete blockage of a coronary artery, leading to a significant part of the heart muscle being starved of blood. This lack of blood flow causes severe damage to the heart muscle.

The most common and notable symptom of STEMI is intense chest pain or discomfort, serving as a critical warning sign.
The reason it's called STEMI is due to its distinctive appearance on an electrocardiogram (ECG). This type of heart attack shows an elevation in the ST segment on the ECG, indicating ongoing damage to the heart muscle during the critical period between its contraction and relaxation.
STEMI is a medical emergency, which requires immediate action to restore blood flow to the heart. This is typically achieved through urgent medical interventions, such as thrombolytic therapy, which involves administering clot-busting drugs, or primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a procedure aimed at opening the blocked arteries.
NSTEMI: A Less Severe But Serious Heart Attack
In contrast, a Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) represents a less severe but still serious type of heart attack. NSTEMI is characterized by a partial or temporary blockage of a coronary artery. This results in reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to less extensive damage compared to what is typically observed in STEMI.
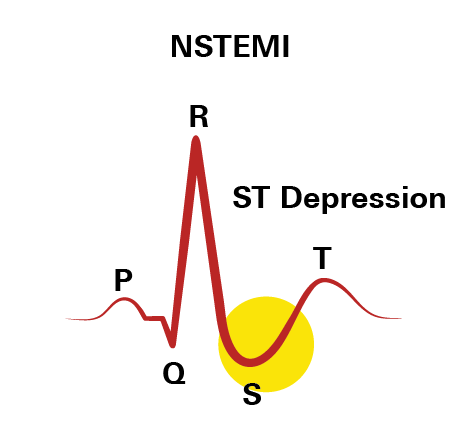
Symptoms of NSTEMI often mirror those of STEMI, including chest pain or discomfort, but are usually less intense. However, the diagnosis of NSTEMI differs on an ECG. In contrast to the ST-segment elevation seen in STEMI, NSTEMI is identified by ST-segment depression or T-wave changes.
The treatment approach for NSTEMI, while still urgent, may not demand the immediate intervention that is characteristic of STEMI. Treatment options for NSTEMI often include a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty may be necessary. The focus is on stabilizing the condition and preventing further deterioration or recurrence of a heart attack.
Common Symptoms to Look Out For
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Often described as a feeling of pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center or left side of the chest. The sensation can last for more than a few minutes or go away and return
- Shortness of Breath: This can occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Other Symptoms:May include breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea, lightheadedness, or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach
Understanding the Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of having a heart attack. Being aware of these can help in prevention and early detection.
- Age: The risk increases for men over 45 and women over 55
- Family History: A family history of heart disease, especially at an early age, increases risk
- High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels: These conditions can lead to artery damage
- Smoking: Smokers have a significantly higher risk of heart attack
- Diabetes: Especially when not well-controlled
- Obesity: Excess weight typically worsens other risk factors
- Physical Inactivity: Regular physical activity is beneficial in controlling other risk factors like obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes
- Poor Diet: A diet high in saturated fat, trans fat, sodium, and cholesterol has been linked to heart disease
What Should You Do?
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack is crucial, regardless of whether it's a STEMI or NSTEMI. Common signs include chest pain, discomfort, shortness of breath, and other heart-related symptoms. It's important to understand that these symptoms demand quick action. If you or someone around you experiences such symptoms, the immediate response can be life-saving.
The first and most critical step is to seek immediate medical help. For both STEMI and NSTEMI, the timing of medical intervention is crucial and can significantly impact the outcome. If you suspect a heart attack, calling emergency services right away is essential.
Another important aspect is understanding and being aware of the risk factors associated with heart attacks. Knowledge of risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and family history is key in both prevention and early detection. Being informed about these risks can guide you in taking proactive steps towards heart health.
Post-heart attack care is also vital. After experiencing a heart attack, adhering to medical advice and prescribed medications is essential. Additionally, making necessary lifestyle changes plays a significant role in preventing the recurrence of heart attacks and in improving overall heart health. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures that recovery is on track and any potential risks are managed effectively.
Summary
sUderstanding the nuances of STEMI and NSTEMI, their symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial. Recognizing a heart attack and responding swiftly can be the difference between life and death. Remember, prevention is key. By managing risk factors and leading a healthy lifestyle, the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack can be significantly reduced.
This guide aims to empower you with knowledge, whether it's for prevention, early detection, or knowing what to do in an emergency. Stay informed, stay prepared, and take care of your heart health.
