Rasagiline (Azilect) - How it work, Uses, & Side Effects
Rasagiline, sold under the brand name Azilect, is a medication used to treat Parkinson's disease, a neurological brain disorder characterized by the gradual loss of muscle control, stiffness, and tremors.
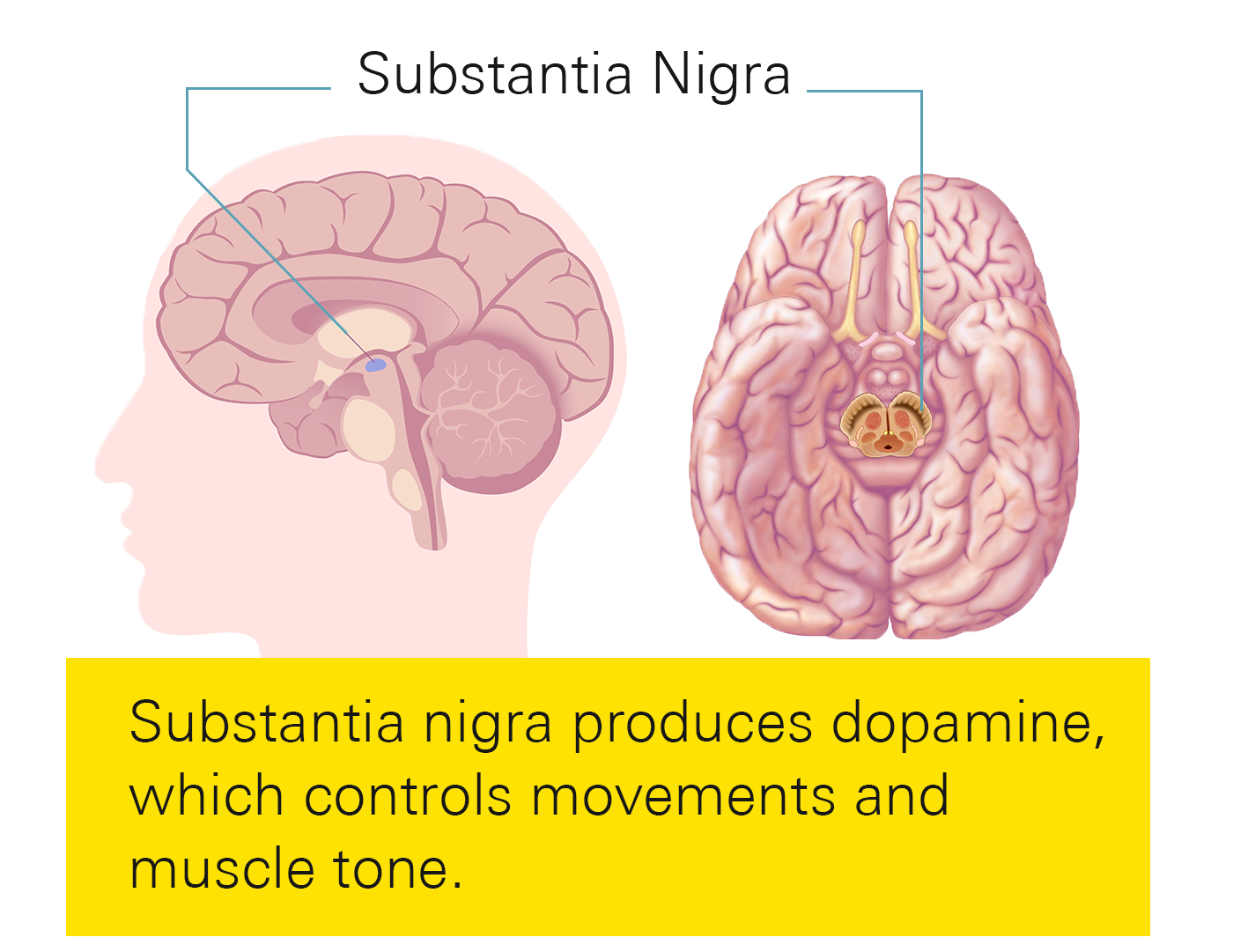
Parkinson’s disease occurs when certain brain cells (neurons) in a region called the substantia nigra, start to die or deteriorate. These neurons produce a chemical called dopamine, which is crucial for smooth and coordinated muscle movements and maintaining balance. Dopamine also helps send movement instructions to other parts of the brain. As dopamine producing cells die off, your movements become jerky and uncoordinated. In simple terms, Parkinson’s disease is caused by a shortage of dopamine in the brain.
Learn about Medication Options for Parkinson's Disease
How Rasagiline Works
Rasagiline increases dopamine levels by blocking the breakdown of dopamine. Rasagiline works by blocking an enzyme in the brain called monoamine oxidase-B (MOA-B) which breaks down dopamine. By inhibiting MOA-B, rasagiline helps to preserve dopamine levels in the brain. With more dopamine available, communication between brain regions responsible for movement improves, leading to a reduction in Parkinson's symptoms, including muscle stiffness and tremors.
It's important to note that while rasagiline can't reverse the damage already done by Parkinson's, it can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life for those living with the condition. So, while it doesn't cure Parkinson's, it's a valuable tool in the ongoing battle against its effects.
Dosage and Administration
Rasagiline is typically prescribed for Parkinson’s disease either on its own (as monotherapy) or alongside other medications. It's usually taken orally, with doses ranging from 0.5 to 1 mg per day.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on factors like your medical history, how well you respond to treatment, and any other medications you might be taking.
You can take rasagiline with or without food, but make sure not to chew, break, or crush the tablets—simply swallow them whole. If you happen to miss a dose, don't double up on the next one. Just take your next scheduled dose as usual.
It's worth noting that the safety and effectiveness of rasagiline haven't been established for individuals under 18 years old.
- With or Without Food: Ranolazine can be taken with or without food.
- Do Not Chew, Break, or Crush: Swallow the tablets whole.
- Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take the next dose at the scheduled time. Do not double the dose to make up for the missed one.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Insomnia or unusual dreams
- Dyskinesia (lack of muscle control/involuntary muscle movement)
- Depressed mood
- Decreased appetite and/or weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Joint pain
- Rash
- Flu-like symptoms (I.e. cough)
Serious side effects include:
- Chest pain
- Blurred vision
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Confusion
- Hallucination
- Extreme fatigue
- Deteriorating signs of Parkinson's disease, particularly uncontrolled muscle movements
Driving and other risky activities should be avoided until you know how rasagiline will impact you. Tiredness or vertigo can lead to severe injuries, fatalities, and/or falls.
Avoid standing up too quickly after sitting or lying down because doing so could make you feel faint.
As a further precaution, it’s recommended to refrain from consuming alcohol, particularly red wine, vermouth, and tap beer or ale.
Interactions
Drug interactions could alter how your medications function or raise the possibility of major negative side effects.
Rasagiline may interact with certain foods and beverages, including aged cheeses, matured cheeses, fava or broad beans, soy sauce, herring, pickled or processed meats, and certain types of fish. These foods contain a compound called tyramine, which can cause a sudden increase in blood pressure when combined with rasagiline. This spike in blood pressure could lead to severe, life-threatening complications. It's crucial to avoid consuming these foods while taking rasagiline and for at least two weeks after stopping the medication.
If you notice any symptoms of serotonin syndrome while taking rasagiline, such as restlessness, hallucinations, fever, sweating, rapid heartbeat, muscle stiffness, twitching, coordination difficulties, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, seek immediate medical attention.
Additionally, it's advisable to avoid products containing caffeine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, or dopamine while on rasagiline.
Rasagiline is broken down in the body by an enzyme called CYP (cytochrome) P450 1A2. Therefore, it's important not to exceed a daily dose of 0.5 mg when taking medications like ciprofloxacin or other CYP1A2 inhibitors, as this could affect how rasagiline is metabolized in the body. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medications to ensure safe and effective treatment.
