What Is a Angiotensin Receptor Blocker?
- Angiotensin II is a hormone that makes blood vessels constrict/narrow. High blood pressure can result from this contriction.
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) reduce your blood pressure by preventing the action of angiotensin II. They are also used to treat kidney disease and heart failure.
- ARBs include azilsartan, candesartan, irbesartan, losartan, olmesartan, telmisartan, valsartan
If you struggle with high blood pressure, heart failure, and/or kidney disease, angiotensin receptor blockers may be the right drug class for you. Angiotensin receptor blockers have been around since the 1970s and are commonly recommended as an initial or add-on antihypertensive therapy.
What are Angiotensin Receptor Blockers?
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), also called angiotensin II blockers/antagonists, are a drug class of medications that commonly end in “-sartan”.
ARBs reduce your blood pressure by preventing the action of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a hormone that makes your blood vessels narrow/constrict. High blood pressure and inadequate kidney blood flow may result from this constriction. Angiotensin II can also cause salt and water retention in your body, which further increases your blood pressure.
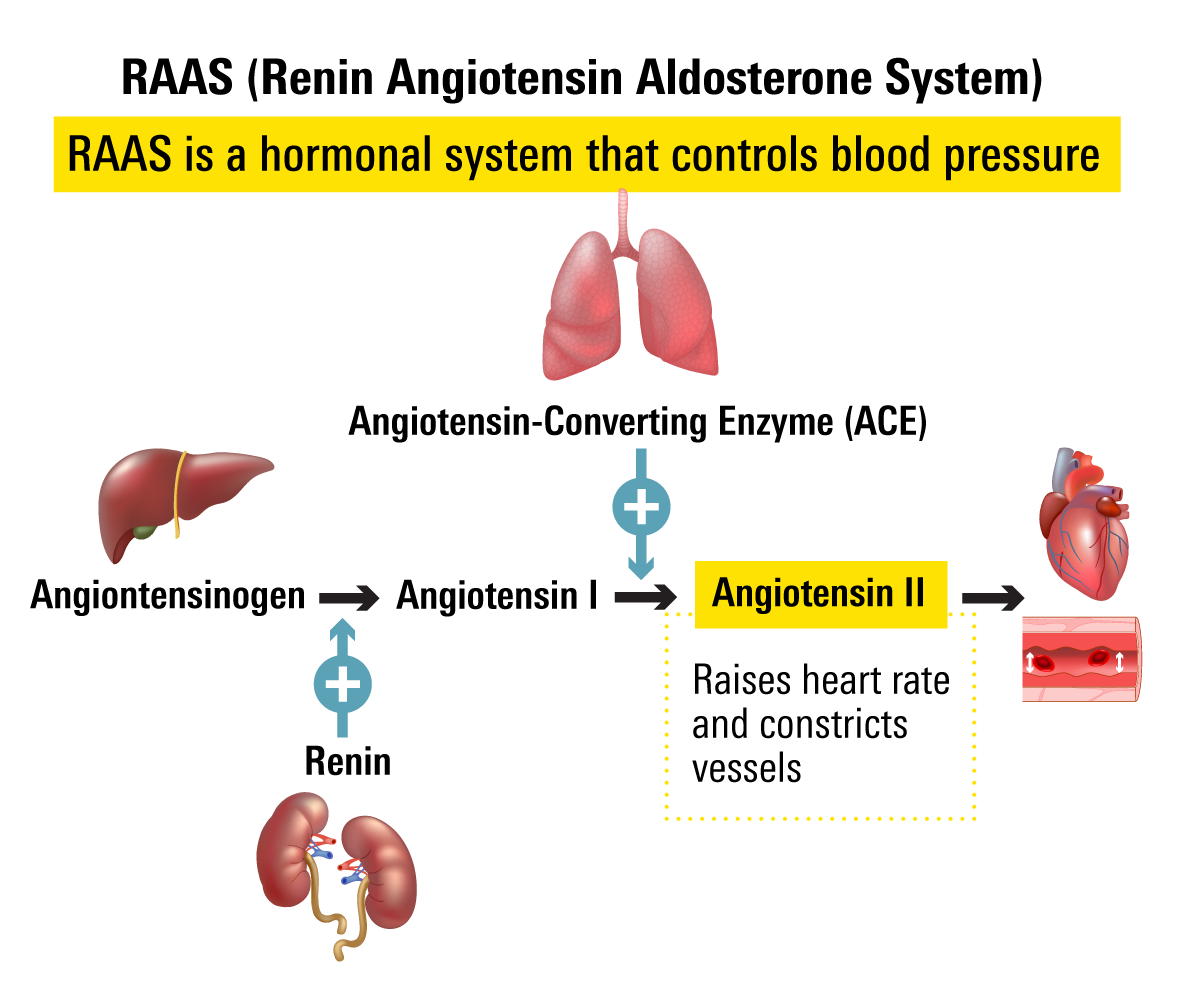
How RAAS (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone) Works
- Renin from kidney converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
- ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) converts angiotensing I to angiotensin II
- Angiotensin II binds to receptors and has constricting effects on blood vessels
Another drug class with similar effects on hypertension is angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ACE inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II—earlier stage of RAAS, whereas ARBs block the receptor that angiotensin II acts on.
Both ARBs and ACE inhibitors dilate/widen your blood vessels to facilitate easier blood flow, which decreases your blood pressure. For individuals who are unable to take ACE inhibitors, ARBs are typically administered.
What are ARBs used for?
ARBs have been shown to be effective in the treatment of:
- Kidney disease caused by diabetes
- Heart failure
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- ARBs may also be recommended for use after a heart attack to limit further damage
ARBs tend to minimize risks of heart attack and stroke as well as delay kidney damage in individuals with impaired kidney function. Additionally, these medications increase the life expectancy of those with heart failure and decrease hospital admissions.
What are Examples of ARBs?
Common ARBs include:
- Azilsartan (brand: Edarbil) 40–80 mg daily
- Candesartan (Atacand) 8–32 mg daily in 1–2 divided doses
- Irbesartan (Avapro) 75–300 mg daily
- Losartan (Cozaar) 25–100 mg daily in 1–2 divided doses
- Olmesartan (Benicar) 10–40 mg daily
May cause sprue-like enteropathy, which is a severe condition involving chronic diarrhea with substantial weight loss. Can occur months to years after drug initiation. - Telmisartan (Micardis) 40–80 mg daily
- Valsartan (Diovan, Prexxartan oral solution) 80–320 mg daily
What are Side Effects of ARBs?
Side effects of ARBs are the same as ACE inhibitors, however, they contain less cough and angioedema (swelling of the area beneath your skin), and do not require a washout period with neprilysin inhibitor called sacubitril/valsartan (brand: entresto).
Common side effects of ARBs include:
- Cough (less than ACE inhibitors)
- Dizziness and/or lightheadedness
- Headache
- Confusion
- Severe vomiting and/or diarrhea
- Muscle cramps or weakness, back or leg pain
- Change of taste in your mouth (metallic or salty)
What Should I Look Out For with ARBs?
ARBs can cause birth defects if taken during pregnancy. Use an effective birth control while taking this medication. If you become pregnant during treatment, stop using this medication and tell your healthcare provider right away.
These medications can increase the amount of potassium in your body. Do not use salt substitutes or potassium supplements while taking this medication, unless your healthcare provider told you to do so.
Get emergency medical help if you have any of the signs of an allergic reaction while taking an ARB: hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of your face, lips, tongue, and/or throat.
What Should I Do if I Miss a Dose?
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it's almost time for your next dose. In this case, skip the forgotten dose and take the next one at the usual time. Do not take 2 doses together to make up for a missed dose.
Speak with your doctor
ARBs have been clinically proven to be effective in decreasing blood pressure and have shown to be well tolerated. Talk to your healthcare provider about using ARBs and send your prescription to Marley Drug. Save up to 95% compared to your local pharmacy by using Marley Drug.
