The Most Dangerous Arrhythmia: Ventricular Fibrillation
What are Arrhythmias?
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that occur when the electrical signals in the heart are disrupted. These disruptions can cause the heart to beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or in an irregular pattern. Arrhythmias can occur in the atria (upper chambers) or the ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart. They can be temporary or chronic and may or may not cause symptoms.
The Typical Heartbeat
In typical adults, the heart beats 60–100 beats per minute (bpm). It involves a sequence of events that occur in a coordinated manner.
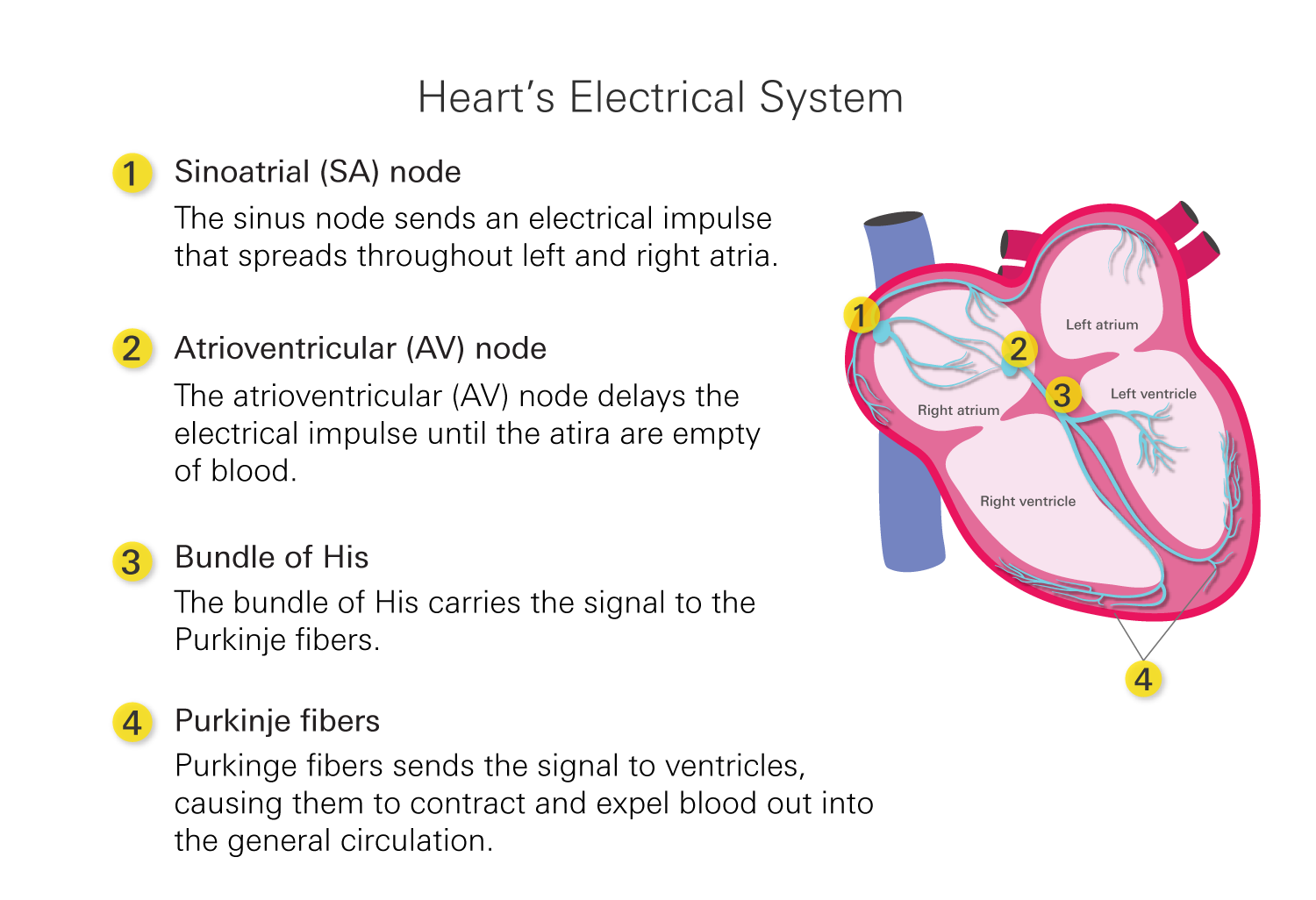
- The heartbeat begins with an electrical signal originating from the sinus node (SA node) in the right atrium. The electrical signal spreads through the atria, causing them to contract and push blood into the ventricles.
- The electrical signal reaches the atrioventricular node (AV node) located between the atria and the ventricles. The AV node briefly delays the electrical impulse, allowing the atria to finish contracting and the ventricles to fill completely with blood.
- Once the ventricles are filled, the electrical signal rapidly travels down the bundle of His and its branches, known as the bundle branches, and reaches the Purkinje fibers.
- The Purkinje fibers distribute the electrical signal simultaneously throughout the ventricles, causing them to contract forcefully. The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta.
What is Ventricular Fibrillation?
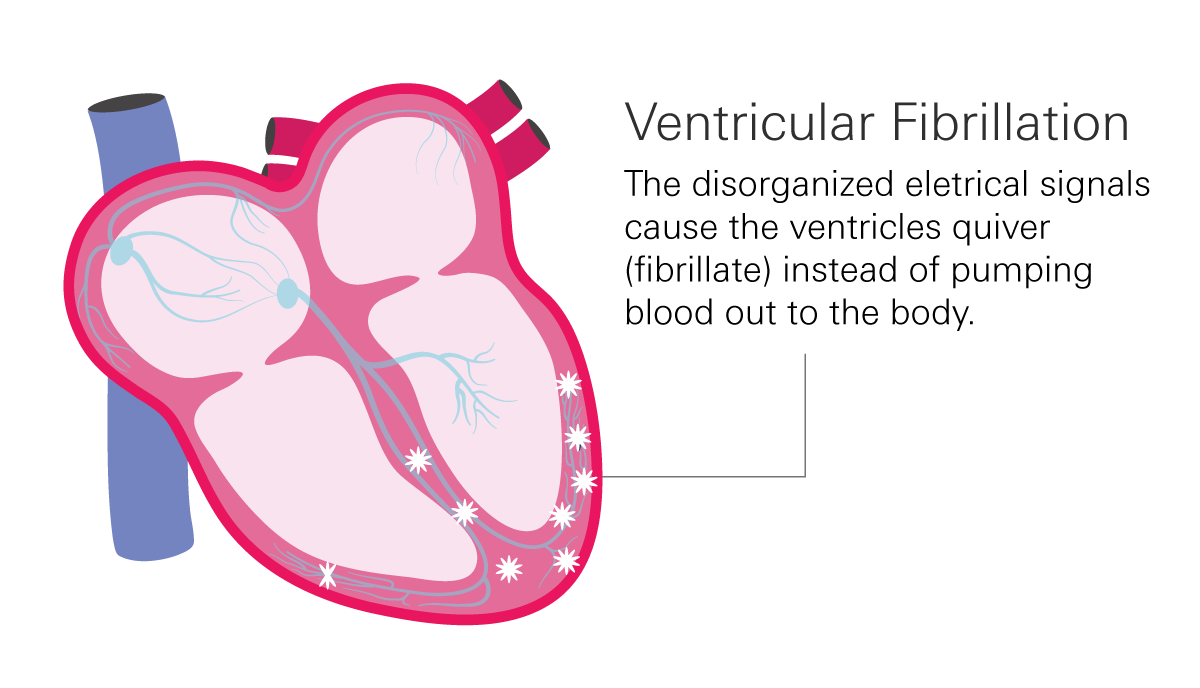
Ventricular fibrillation, or “V fib” is considered the most dangerous type of arrythmia. Instead of squeezing and pumping blood to the lungs and body, the ventricles just quiver and flutter in a rapid, uncoordinated, and chaotic manner.
During ventricular fibrillation, the heart's electrical signals become disorganized, leading to the loss of synchronized contraction and effective pumping action. V fib is a medical emergency because it can cause sudden cardiac arrest, leading to loss of consciousness and death if not promptly treated.
Causes of Ventricular Fibrillation
In many individuals, the exact cause of ventricular fibrillation is unknown. However, there are many possible factors that increase the risk of directly result in the condition, including:
- Blockage of blood flow to the heart
- Toxicity from medications
- Other arrhythmias
- Electrocution or other serious incidents
Electrocution can disrupt the normal electrical activity of your heart resulting in V fib. Interestingly, it is also possible for the heart’s conduction to be disturbed by physical incidents, such as aggressive collisions during contact sports.
Certain conditions, such as coronary artery disease and heart attacks, can disrupt the regular blood flow and make the heart more electrically unstable and prone to arrhythmias, such as V fib.
Certain medications can produce side effects that put you at increased risk of experiencing an arrhythmia. This could include medications that reduce your potassium levels (thiazide diuretics) or medications that directly cause certain arrhythmias.
There are certain arrhythmias that can ultimately progress into V fib. One arrhythmia in particular, QT prolongation, can lead to another arrhythmia (Torsade de pointes), which, when left untreated, often results in V fib.
Symptoms of Ventricular Fibrillation
It is often difficult to recognize ventricular fibrillation until it becomes a serious cardiac event. The most commonly experienced symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath, even possibly gasping for breath
- Feeling of “fluttering” or palpitations in your chest
- Suddenly collapsing
- Cardiac arrest (no pulse)
Treatment for Ventricular Fibrillation
There are two stages to treatment for ventricular fibrillation. The first is the acute treatment to imminently restore normal rhythm. Once this acute risk is gone, the next stage is the prevention of future attacks of ventricular fibrillation.
Acute treatment
Call 911
V fib is a medical emergency, and it is important for trained medical professionals to arrive and take control of the situation.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
The actions of CPR provide physical compressions of the heart, forcibly pushing on the heart to squeeze blood throughout the body. This maintains blood flow throughout the tissues of your body until further help arrives.
Defibrillation
Defibrillation is an electrical shock to the system that almost “resets” the heart. This allows your heart’s conduction system an opportunity to restart normal electrical activity.
Medications
Depending on the cause of the attack of V fib, certain medications are sometimes administered in order to counteract the arrhythmia and bring you back into a normal heart rhythm.
Chronic prevention
Prescription medication
- Beta blockers
Beta blockers such as metoprolol and bisoprolol have been found to have efficacy in suppressing arrhythmias, including V fib. - Anti-arrhythmic medications (class IA, IB, III)
Certain anti-arrhythmic medications are also often prescribed in order to suppress the part of the heart’s conduction that is thought to be causing this ventricular fibrillation.
Implantable device
A common intervention is the placement of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) device. This device works by monitoring your heart’s rhythm, and if any arrhythmia is detected an electric shock is sent to your heart to shift your heart back to a normal rhythm.
Surgery
If the arrhythmia is thought to be due to a physical anomaly, it can sometimes be corrected with surgery on your heart.
Why it is so Important to Take Your V Fib Medications
It is essential to take all precautions to prevent V fib if you are at known risk. This may include ensuring you adhere to a strict medication regimen. While surgery and implantable devices take some of the responsibility out of your hands, medications are up to you to stay on top of. Missing even a single dose of these medications can put you at risk of dysregulation and therefore another attack of V fib.
References
- V-fib: What is it, causes, symptoms & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Retrieved April 16, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2022, October 28). Ventricular fibrillation. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved April 16, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- Ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular Fibrillation | Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2021, June 14). Retrieved April 16, 2023, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org
